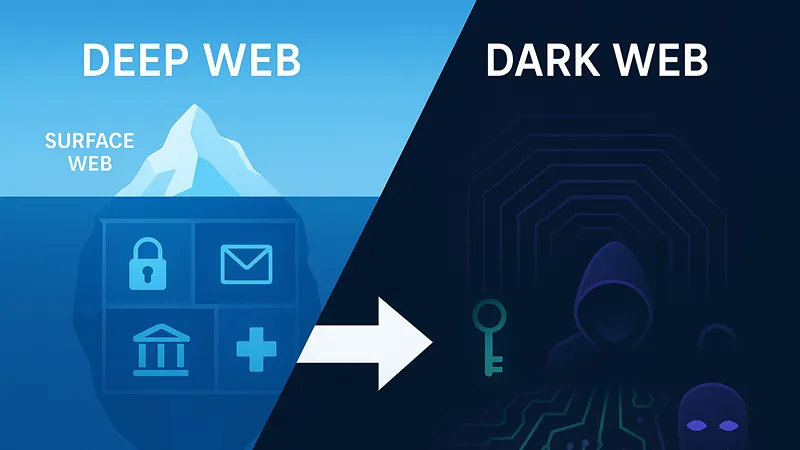
The internet you use every day – with its search engines, social media, and news sites – is just the tip of the iceberg. This visible layer is known as the surface web. But beneath it lies a much larger, hidden world, often misunderstood under the umbrella term “dark web.” However, the key distinction lies in the deep web vs dark web debate. They are not the same thing, and understanding their differences is important for your online privacy and security.
So, what is the deep web? This is the largest part of the internet, consisting of all content not indexed by standard search engines. It is mostly benign and used by everyone. This includes your private email inbox, online banking portals, medical records, corporate databases, and subscription-based content. Essentially, it’s any page behind a login, paywall, or password. The deep web is private but not inherently nefarious.
In contrast, the dark web is a small, intentionally hidden subsection of the deep web. Accessing it requires specific software, like the Tor browser, which anonymizes user traffic. While the dark web itself is a tool for privacy, its anonymity also makes it a haven for both legal and illegal activities. It’s crucial to understand the deep web vs dark web distinction: one is mostly private and safe, while the other requires caution due to potential cybersecurity risks and illicit marketplaces.
Understanding the deep web vs dark web is essential for anyone concerned with digital ethics and protecting their personal data online. While you use the deep web daily without issue, navigating the dark web demands a strong awareness of the potential dangers involved.
What’s the Deep Web?

The deep web refers to all online content that is not indexed by traditional search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo. This means you can’t simply type in a query and find these pages in search results. The deep web makes up the majority of the internet – roughly 90–95%—and exists primarily to protect sensitive information and provide secure access to data.
This hidden section of the web includes password-protected portals, subscription-only resources, and databases that require special permissions. Contrary to popular belief, the deep web is not inherently suspicious or illegal. Instead, it’s a vital layer of the internet that supports everyday online activities.
Examples of deep web content you use daily:
- Email Accounts: Gmail or Outlook inboxes that require secure login.
- Online Banking: Financial dashboards with encrypted customer data.
- Streaming Services: Platforms like Netflix, Hulu, or Disney+ that use subscription-based access.
- Academic Databases: Research articles and e-libraries locked behind institutional or paid access.
- Corporate Networks: Internal company intranets, tools, and project management systems.
The deep web ensures that personal, financial, and institutional data remains safe from public exposure. Without it, sensitive records like medical histories or financial transactions could be freely accessible to anyone. Accessing the deep web is not only legal but also necessary in order to maintain digital privacy and security.
What’s the Dark Web?

The dark web is a much smaller, deliberately concealed part of the deep web. Unlike the deep web’s everyday secure sites, the dark web is intentionally hidden and requires special software such as Tor (The Onion Router) or I2P (Invisible Internet Project) to access. These tools anonymize user identities by routing traffic through multiple encrypted layers, making it difficult to trace who is visiting or operating a site.
The dark web has a dual reputation. On one hand, it provides a safe haven for journalists, whistle-blowers, and activists working under oppressive regimes, allowing them to share information anonymously. On the other hand, it is also notorious for hosting illegal marketplaces and criminal activity, including the trade of stolen data, counterfeit documents, drugs, and even weapons.
Key features of the dark web include
- Restricted Access: Unlike the deep web, you cannot access it through a normal browser. Specialized tools are mandatory.
- Anonymity: Every interaction is designed to mask identities, making it appealing to both privacy advocates and cybercriminals.
- Content Variety: Includes forums for political activism, but also marketplaces selling illegal goods and services.
- Risks: Dark web sites often contain scams, malware, and traps set up by cybercriminals or even law enforcement.
Although merely visiting the dark web is not illegal in itself, the activities that occur there can cross legal boundaries. Caution is essential, as the environment poses significant security risks even for experienced users.
Deep Web vs Dark Web – Key Differences
| Feature | Deep Web | Dark Web |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Standard browsers (with login) | Requires Tor or similar tools |
| Indexing | Not indexed by search engines | Not indexed and intentionally hidden |
| Legality | Legal and widely used | Mixed – can include illegal content |
| Purpose | Privacy, restricted access | Anonymity, secrecy |
| Risk Level | Low (if accessed properly) | High (due to malware, scams, etc.) |
| Examples | Gmail, online banking, Netflix | Silk Road, hidden forums |
Online Safety Tips for Deep and Dark Web Users
Whether you’re accessing the deep web for legitimate reasons or exploring the dark web for research, it’s essential to follow robust safety practices to protect your identity, data, and devices. Here are some expanded tips to help you stay secure:
- Use a VPN to encrypt your internet connection and mask your IP address. This adds an extra layer of anonymity and helps prevent tracking by third parties.
- Keep your antivirus software and operating system updated to defend against malware, spyware, and other vulnerabilities that may be present on dark web sites.
- Never share personal information such as your real name, address, phone number, or financial details on anonymous platforms. Use pseudonyms and avoid linking accounts to your real identity.
- Avoid downloading unknown files or clicking suspicious links, as these may contain malware or lead to phishing scams. Always verify the source before interacting with any content.
- Use secure browsers like Tor for dark web access, and configure them properly to avoid leaks. Disable scripts and plugins that could compromise your anonymity.
- Consider using virtual machines or sandbox environments when exploring the dark web to isolate potential threats from your main system.
- Be cautious of scams and fake marketplaces. If something seems too good to be true, it probably is. Trust only verified sources and communities.
- Regularly clear your browser cache and cookies to minimize tracking and data retention.
- Avoid using your primary email address. Instead, create disposable or encrypted email accounts for dark web interactions.
- Educate yourself continuously about cybersecurity best practices and stay informed about emerging threats and tools.